Understanding the Stock Market: A Beginner's Guide
The stock market is a complex yet fascinating realm where fortunes are made and lost, opportunities abound, and risks lurk around every corner. For beginners, the stock market can seem daunting and impenetrable, but with the right knowledge and approach, it can become an exciting and rewarding venture. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the stock market by explaining its basic concepts, how it operates, and essential tips for beginners.
What is Stock Market?
The stock market refers to the collection of markets and exchanges where activities related to buying, selling, and issuance of shares of publicly-held companies take place. These financial activities are conducted through institutionalized formal exchanges or over-the-counter (OTC) marketplaces which operate under a defined set of regulations.
Key Components of Stock Market
1.Stock Exchanges:
Stock exchanges are centralized platforms where stocks are listed and traded. The most well-known stock exchanges include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), NASDAQ, and the London Stock Exchange (LSE). These exchanges provide a transparent and regulated environment for the trading of stocks.
2.Stock Shares:
Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you purchase a stock, you are buying a piece of that company and becoming a shareholder. Stocks are issued by companies to raise capital for various purposes, such as expanding operations, developing new products, or paying off debt.
3.Indices:
Indices are statistical measures that track the performance of a group of stocks. Common indices include the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), and the NASDAQ Composite. These indices provide a snapshot of the overall market performance and can serve as benchmarks for investment portfolios.
2. How the Stock Market Works?
The stock market operates through a network of exchanges. Companies list their shares on an exchange through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). Investors can then buy and sell these shares among themselves, and the exchange tracks the supply and demand for each listed stock. The price of a stock is determined by the supply and demand dynamics in the market.
Key Players:
1.Individual Investors:-
These are people like you and me who buy and sell stocks. Individual investors can participate in the stock market through brokerage accounts, either online or through traditional brokerage firms.
2.Institutional Investors:-
These include pension funds, mutual funds, insurance companies, and hedge funds, which invest large amounts of money in the stock market. Institutional investors often have significant influence on market movements due to the large volumes of trades they execute.
3.Market Makers:-
Market makers are firms or individuals that provide liquidity by buying and selling stocks at publicly quoted prices. They play a crucial role in ensuring that there is always a buyer or seller for a stock, thereby facilitating smooth and efficient trading.
Why do companies issue Stock?

Companies issue stock to raise capital for various purposes, such as expanding operations, developing new products, or paying off debt. By selling shares to the public, companies can access a large pool of investors and avoid the costs and restrictions of borrowing money from banks. Issuing stock also allows companies to share ownership and potential profits with investors.
Types of Stocks:-
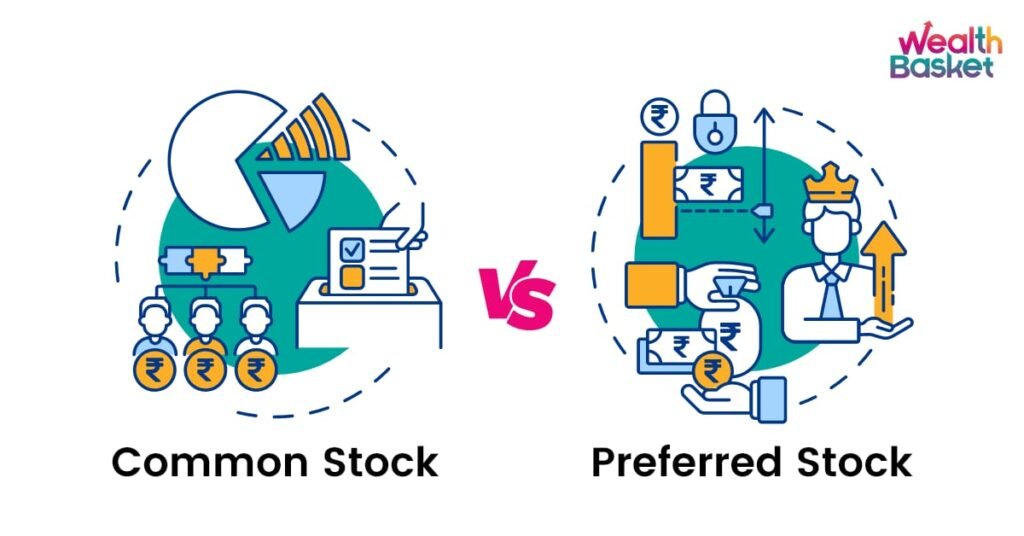
1.Common Stocks
Common stocks represent ownership in a company and entitle the holder to a share of the company’s profits through dividends and/or capital appreciation. Common stockholders typically have voting rights, allowing them to participate in corporate governance by voting on key issues such as electing the board of directors.
2.Preferred Stocks
Preferred stocks provide a higher claim on assets and earnings than common stocks. Preferred stockholders receive dividends before common stockholders and have a priority claim on assets in the event of liquidation. However, they usually do not have voting rights. Preferred stocks are often seen as a hybrid between stocks and bonds, offering a fixed dividend payment like bonds and potential for capital appreciation like stocks.
How to Invest in Stocks?
STEP-1 Open a Brokerage account
To buy and sell stocks, you need to open a brokerage account. There are many online brokers available that offer different services and fee structures. Some of the most popular ones include:
These brokers provide a range of services including financial advice, retirement planning, and research. Full-service brokers typically charge higher fees but offer personalized service and expert advice. Examples include Merrill Lynch and Morgan Stanley.
These brokers offer lower fees and fewer services. Discount brokers provide essential trading services and access to research tools but do not offer personalized financial advice. Examples include Charles Schwab, E*TRADE, and Robinhood.
STEP-2 Research and Choose Stocks

Before investing, it’s important to research and choose stocks wisely. Here are some factors to consider:
– **Company Performance:** Look at the company’s financial statements, including revenue, profit margins, and debt levels. A company with strong and consistent financial performance is generally a good candidate for investment.
– **Industry Trends:** Consider the overall trends and growth potential in the industry the company operates in. Industries with strong growth prospects can provide attractive investment opportunities.
– **Valuation:** Assess whether the stock is fairly priced using metrics like the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio, and Dividend Yield. Comparing these metrics with industry averages can help determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued.
– **Management:** Evaluate the company’s management team and their track record. Strong leadership can significantly impact a company’s performance and growth prospects.
– **Competitive Position:** Analyze the company’s competitive position within its industry. Companies with a strong market position and competitive advantages are more likely to succeed in the long term.
STEP-3 Diversify Your Portfolio

Diversification involves spreading your investments across various assets to reduce risk. By holding a mix of stocks from different industries, sectors, and geographies, you can protect your portfolio from significant losses if one particular area underperforms. Diversification can be achieved through individual stock selection or by investing in mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that provide broad market exposure.
STEP-4 Understanding Stock Market Terms

Here are some common terms you’ll encounter:
– **Bull Market:** A period during which stock prices are rising, often characterized by investor optimism and economic growth. Bull markets can last for months or even years and are typically associated with strong corporate earnings and positive economic indicators.
– **Bear Market:** A period during which stock prices are falling, often characterized by investor pessimism and economic decline. Bear markets can be triggered by various factors, such as economic recessions, geopolitical events, or financial crises.
– **Dividends:** Payments made by a company to its shareholders, usually from profits. Dividends provide a regular income stream for investors and can be an important component of total returns.
– **Capital Gains:** The profit made from selling a stock for more than you paid for it. Capital gains can be short-term (held for less than a year) or long-term (held for more than a year), with different tax implications for each.
– **Blue-Chip Stocks:** Shares in large, reputable companies with a history of stable earnings and reliable dividend payments. Blue-chip stocks are often considered safe and reliable investments, suitable for conservative investors.
Stock Market Strategies
There are various strategies that investors use to make money in the stock market. Here are a few:
1. Buy and Hold
This strategy involves buying stocks and holding them for a long period, regardless of market fluctuations. The idea is that the stock market tends to increase in value over the long term, despite short-term volatility. Buy-and-hold investors focus on the long-term potential of their investments and are less concerned with short-term price movements.
2. Dollar-Cost Averaging
This strategy involves regularly investing a fixed amount of money in a particular stock or portfolio, regardless of its price. By doing this, you buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when prices are high, potentially reducing your average cost per share. Dollar-cost averaging can help mitigate the impact of market volatility and reduce the emotional stress of investing.
3. Dividend Investing
This strategy focuses on buying stocks that pay high and stable dividends. Investors reinvest these dividends to buy more shares, compounding their returns over time. Dividend investing can provide a steady income stream and reduce the reliance on capital gains for returns. This strategy is particularly popular among retirees and conservative investors seeking regular income.
4. Growth Investing
Growth investing involves investing in companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies. These companies often reinvest their earnings to expand operations, develop new products, and enter new markets. Growth investors seek capital appreciation rather than income and are willing to accept higher volatility in exchange for the potential for significant gains.
5.Value Investing
Value investing involves finding undervalued stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value. Value investors look for companies with strong fundamentals, such as low P/E ratios, high dividend yields, and strong balance sheets. This strategy requires patience and a long-term perspective, as it may take time for the market to recognize the true value of these stocks.
Risks and Rewards

Investing in the stock market comes with risks and rewards. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions.
Risks:
– **Market Risk:** The risk of losing money due to overall market declines. Market risk is influenced by factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and geopolitical events.
– **Company Risk:** The risk that a specific company will perform poorly. This risk can be mitigated through diversification and thorough research.
– **Liquidity Risk:** The risk that you may not be able to sell your stocks quickly without impacting the stock price. Stocks with low trading volumes may be more susceptible to liquidity risk.
– **Interest Rate Risk:** The risk that changes in interest rates will negatively impact stock prices. Higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs for companies and reduce consumer spending, leading to lower corporate earnings.
– **Inflation Risk:** The risk that rising inflation will erode the purchasing power of your investments. Inflation can reduce the real value of future cash flows and dividends.
Rewards:
– **Potential for High Returns:** Historically, the stock market has provided higher returns than many other types of investments, such as bonds or savings accounts. Stocks have the potential for significant capital appreciation and dividend income.
– **Dividends:** Regular payments from profitable companies can provide a steady income stream. Dividends can be reinvested to compound returns over time.
– **Ownership:** Owning stocks means you own a part of the company, giving you voting rights and a share in its profits. Shareholders can influence corporate decisions through their voting rights.
– **Inflation Hedge:** Stocks can act as a hedge against inflation, as companies can increase prices and revenues in response to rising costs.
The Role of Economic Indicators
– **Gross Domestic Product (GDP):** Measures the total economic output of a country. A growing GDP often leads to higher corporate earnings and stock prices. Strong GDP growth indicates a healthy economy and increased consumer spending.
– **Unemployment Rate:** Indicates the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. High unemployment can negatively impact consumer spending and corporate profits. Conversely, low unemployment suggests a strong labor market and increased consumer confidence.
– **Inflation:** Measures the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. Moderate inflation is typically good for the stock market, as it indicates a growing economy. However, high inflation can erode purchasing power and profits, leading to lower stock prices.
– **Interest Rates:** Set by central banks, interest rates influence borrowing costs and consumer spending. Lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth and increase stock prices, while higher interest rates can have the opposite effect.
– **Consumer Confidence Index (CCI):** Measures the degree of optimism that consumers feel about the overall state of the economy and their personal financial situation. Higher consumer confidence can lead to increased spending and higher corporate earnings.
– **Retail Sales:** Track consumer spending on goods and services. Strong retail sales indicate robust consumer demand and can boost stock prices.
Common Mistakes to avoid

Here are some common mistakes that beginners should avoid:
– **Lack of Research:** Not doing enough research before investing can lead to poor investment decisions. It’s essential to thoroughly research and understand the companies you invest in.
– **Emotional Investing:** Making decisions based on emotions rather than logic and research can lead to losses. Fear and greed are common emotions that can drive irrational investment decisions.
– **Overtrading:** Frequently buying and selling stocks can rack up fees and reduce overall returns. Overtrading can also lead to short-term focus and increased stress.
– **Ignoring Diversification:** Failing to diversify your portfolio can expose you to unnecessary risk. Diversification helps spread risk across different assets and reduces the impact of individual stock performance on your overall portfolio.
– **Chasing Performance:** Investing in stocks or funds based on recent performance can lead to poor outcomes. Past performance is not indicative of future results, and high-performing stocks may be overvalued.
– **Timing the Market:** Attempting to time the market by predicting short-term price movements is challenging and often unsuccessful. It’s better to focus on long-term investment goals and maintain a disciplined approach.
Getting Started with Stock Market Simulators
For those new to investing, stock market simulators can be a great way to practice without risking real money. These simulators use real market data to allow users to create and manage a virtual portfolio. Some popular stock market simulators include:
– **Investopedia Simulator:** Offers a comprehensive trading experience with real-time data and educational resources. Users can participate in trading contests and track their performance against other investors.
– **Wall Street Survivor:** Provides a fun and interactive way to learn about investing. Users can complete investment challenges and earn virtual rewards.
– **MarketWatch Virtual Stock Exchange:** Allows users to create and manage virtual portfolios with real-time market data. The platform also offers educational articles and investment tips.
Stock market simulators can help beginners build confidence and develop their investment strategies before committing real money.
Continuing Education
The stock market is constantly evolving, and continuing education is crucial for success. Here are some resources to consider:
– **Books:** Some classic investing books include “The Intelligent Investor” by Benjamin Graham, “A Random Walk Down Wall Street” by Burton G. Malkiel, and “Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits” by Philip Fisher. These books provide valuable insights into investment principles and strategies.
– **Online Courses:** Websites like Coursera, Khan Academy, and Udemy offer free and paid courses on investing and finance. These courses cover topics such as stock market fundamentals, technical analysis, and portfolio management.
– **Financial News:** Stay informed by following financial news outlets like CNBC, Bloomberg, Reuters, and The Wall Street Journal. These sources provide up-to-date information on market trends, economic indicators, and company performance.
– **Investment Blogs and Forums:** Participate in online communities like Seeking Alpha, The Motley Fool, and Reddit’s r/investing. These platforms offer a wealth of information and allow you to interact with other investors and experts.
– **Podcasts and Webinars:** Listen to podcasts and webinars hosted by investment experts and financial professionals. Some popular investment podcasts include “The Investors Podcast,” “Motley Fool Money,” and “Invest Like the Best.”
Conclusion
Understanding the stock market is essential for anyone looking to grow their wealth through investing. While it can be complex and intimidating at first, with the right knowledge and approach, you can navigate the stock market with confidence. Remember to do your research, diversify your portfolio, and continue learning to make informed and successful investment decisions.
By following this guide, beginners can start their journey into the stock market equipped with the fundamental knowledge needed to make smart investment choices. Happy investing!
For any Purchases related to Kitchen Essentials-Click here
Videos related to our products- Click here