The Basics of Cryptocurrency Investing

Cryptocurrency has become a buzzword in the world of finance, technology, and investment over the past decade. From the meteoric rise of Bitcoin to the advent of numerous altcoins and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, the cryptocurrency market offers both exciting opportunities and significant risks. For beginners looking to dive into the world of crypto investing, it’s essential to understand the basics. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a solid foundation for anyone interested in cryptocurrency investing, covering fundamental concepts, the different types of cryptocurrencies, how to invest, and strategies to manage risk.
1. Understanding Cryptocurrency
1.1 What is Cryptocurrency?

Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers, ensuring transparency and security.
1.2 Key Features of Cryptocurrencies
– **Decentralization:** Cryptocurrencies are typically decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by any single entity such as a central bank or government. This decentralization is achieved through blockchain technology.
– **Transparency:** All transactions are recorded on a public ledger (the blockchain), which anyone can view. This transparency helps prevent fraud and manipulation.
– **Security:** Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. This makes them highly secure and resistant to hacking.
– **Immutability:** Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures the integrity of the transaction history.
– **Anonymity:** While transactions are transparent, the identities of the parties involved are often pseudonymous, providing a degree of privacy.
1.3 The Evolution of Cryptocurrencies
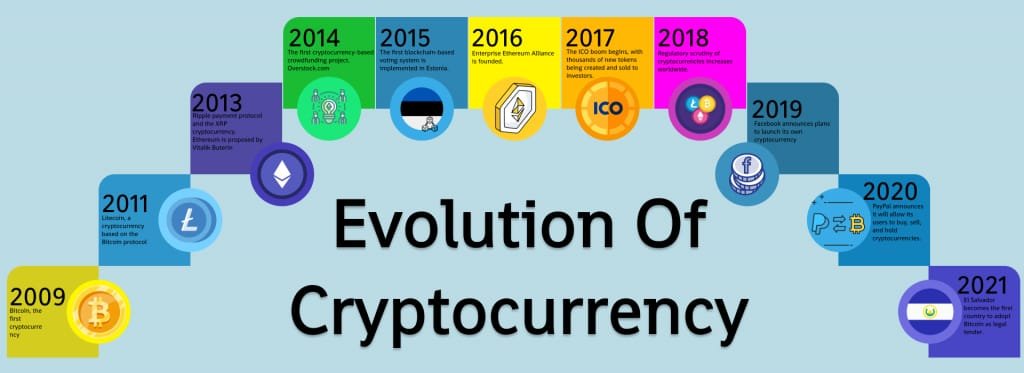
The concept of digital currency has been around since the 1980s, but it wasn’t until the creation of Bitcoin in 2009 by an anonymous person (or group) known as Satoshi Nakamoto that cryptocurrencies gained widespread attention. Since then, thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins) have been developed, each with unique features and use cases.
2.Types of Cryptocurrency
2.1 Bitcoin (BTC)

Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency. It was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, allowing users to send and receive payments without the need for a trusted third party. Bitcoin’s limited supply (capped at 21 million coins) and increasing adoption have contributed to its status as “digital gold.”
2.2 Ethereum (ETH)

Ethereum is a decentralized platform that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. Unlike Bitcoin, which is primarily a digital currency, Ethereum focuses on programmable transactions.
2.3 Altcoins
Altcoins refer to all cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. Some notable altcoins include:
– **Ripple (XRP):** Designed for fast and low-cost cross-border payments.
– **Litecoin (LTC):** Created as the “silver” to Bitcoin’s “gold,” offering faster transaction times and a different hashing algorithm.
– **Cardano (ADA):** Focuses on scalability, sustainability, and interoperability within the blockchain space.
– **Polkadot (DOT):** Aims to enable different blockchains to interoperate and share information.
2.4 Stablecoins

Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to a fiat currency, such as the US dollar. Examples include Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Dai (DAI). Stablecoins aim to provide the benefits of cryptocurrencies without the volatility.
2.5 DeFi Tokens

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to a movement that uses blockchain technology to recreate traditional financial systems such as lending, borrowing, and trading in a decentralized manner. DeFi tokens, such as Uniswap (UNI) and Aave (AAVE), are integral to these platforms and provide various functionalities, including governance and staking.
How to Invest in Cryptocurrencies

3.1 Setting Up a Cryptocurrency Wallet

A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that allows you to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. There are different types of wallets, each with its own pros and cons:
– **Hot Wallets:** These are online wallets that are connected to the internet. They are convenient for frequent transactions but are more vulnerable to hacking. Examples include web wallets (like those on exchanges) and mobile wallets.
– **Cold Wallets:** These are offline wallets that are not connected to the internet, making them more secure. Examples include hardware wallets (like Ledger and Trezor) and paper wallets.
3.2 Choosing a Cryptocurrency Exchange

Cryptocurrency exchanges are platforms where you can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. When choosing an exchange, consider factors such as security, fees, user experience, and the variety of cryptocurrencies offered. Some popular exchanges include:
– **Coinbase:** Known for its user-friendly interface and strong security measures, making it a good choice for beginners.
– **Binance:** Offers a wide range of cryptocurrencies and advanced trading features.
– **Kraken:** Known for its robust security and low fees.
3.3 Conducting Research

Before investing in any cryptocurrency, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research. Here are some factors to consider:
– **Technology:** Understand the underlying technology and use case of the cryptocurrency.
– **Team:** Investigate the team behind the project, their background, and their track record.
– **Community:** Look at the size and engagement of the community supporting the cryptocurrency.
– **Market Cap and Volume:** Check the market capitalization and trading volume to gauge the size and liquidity of the cryptocurrency.
– **Roadmap:** Review the project’s roadmap and milestones to understand its future plans and potential for growth.
3.4 Making Your First Purchase
Once you’ve done your research and chosen a cryptocurrency to invest in, you can make your first purchase. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- **Deposit Funds:** Transfer funds (fiat currency) to your chosen exchange using a bank transfer, credit card, or other payment methods.
- **Place an Order:** Select the cryptocurrency you want to buy and place an order. You can place a market order (buy at the current market price) or a limit order (set a specific price at which to buy).
- **Store Your Cryptocurrency:** After purchasing, transfer your cryptocurrency to your wallet for safekeeping.
4. Cryptocurrency Investment Strategies
4.1 Long-Term Investing (HODLing)
HODLing refers to holding onto your cryptocurrencies for an extended period, regardless of market fluctuations. This strategy is based on the belief that the value of cryptocurrencies will increase significantly over the long term.
4.2 Trading
Cryptocurrency trading involves buying and selling cryptocurrencies to take advantage of short-term price movements. Traders use various strategies, such as:
– **Day Trading:** Buying and selling within the same day to profit from intraday price movements.
– **Swing Trading:** Holding onto a cryptocurrency for several days or weeks to capitalize on expected price swings.
– **Scalping:** Making multiple trades within a day to profit from small price changes.
4.3 Staking
Staking involves holding a cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network. In return, you earn rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency. This strategy is commonly used with proof-of-stake (PoS) cryptocurrencies like Cardano (ADA) and Polkadot (DOT).
4.4 Yield Farming
Yield farming is a DeFi strategy where you lend or stake your cryptocurrencies in exchange for interest or rewards. Platforms like Aave, Compound, and Uniswap offer yield farming opportunities.
4.5 Diversification
Diversifying your cryptocurrency portfolio involves investing in a variety of cryptocurrencies to spread risk. This strategy can help mitigate losses if one cryptocurrency performs poorly.
5. Risks of Cryptocurrency Investing

5.1 Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are known for their extreme price volatility. While this volatility can lead to significant gains, it can also result in substantial losses.
5.2 Regulatory Risks
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Governments around the world are developing frameworks to regulate cryptocurrencies, which can impact their value and use.
5.3 Security Risks
Cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets are targets for hackers. While security measures have improved, there have been numerous instances of exchanges being hacked and funds being stolen.
5.4 Market Manipulation
The cryptocurrency market is relatively unregulated compared to traditional financial markets, making it susceptible to manipulation. Practices such as pump-and-dump schemes can artificially inflate the price of a cryptocurrency, leading to losses for unsuspecting investors.
5.5 Technological Risks
Cryptocurrencies rely on complex technology, and any vulnerabilities or bugs in the code can lead to significant issues. Additionally, advancements in technology could render certain cryptocurrencies obsolete.
5.6 Lack of Consumer Protections
Unlike traditional financial systems, the cryptocurrency market lacks consumer protections. If you lose access to your wallet or fall victim to a scam, there is often no recourse to recover your funds.
6. Tips for Successful Cryptocurrency Investing

6.1 Educate Yourself
Investing in cryptocurrencies requires a good understanding of the technology and market dynamics. Continuously educate yourself through articles, books, online courses, and forums.
6.2 Start Small
If you’re new to cryptocurrency investing, start with a small amount of money that you can afford to lose. As you gain experience and confidence, you can gradually increase your investment.
6.3 Stay Informed
Stay up-to-date with the latest news and developments in the cryptocurrency market. Follow reputable sources and join online communities to stay informed about market trends and potential opportunities.
6.4 Use Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the cryptocurrency’s price. This strategy can help reduce the impact of market volatility and lower the average cost of your investments over time.
6.5 Keep Emotions in Check
The cryptocurrency market can be highly emotional, with extreme price swings leading to fear and greed. It’s essential to keep your emotions in check and make investment decisions based on logic and research rather than impulsive reactions.
6.6 Secure Your Investments
Ensure the security of your investments by using reputable wallets and exchanges. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) and use strong, unique passwords for your accounts. Consider using a hardware wallet for long-term storage of your cryptocurrencies.
7. The Future of Cryptocurrency Investing

7.1 Institutional Adoption
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and large corporations, are increasingly investing in cryptocurrencies. This institutional adoption is expected to bring more stability and credibility to the market.
7.2 Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central banks around the world are exploring the development of digital versions of their fiat currencies, known as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). CBDCs could integrate with existing cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, driving further adoption and innovation.
7.3 Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is revolutionizing traditional financial systems by offering decentralized alternatives to banking, lending, and trading. The growth of DeFi platforms and tokens is expected to continue, providing new investment opportunities and financial services.
7.4 Regulatory Developments
As the cryptocurrency market matures, governments are developing regulatory frameworks to ensure investor protection and market stability. While regulation may introduce challenges, it can also provide legitimacy and foster wider adoption.
7.5 Technological Advancements
Advancements in blockchain technology, scalability solutions, and interoperability between different blockchain networks will drive the evolution of cryptocurrencies. These technological improvements will enhance the functionality and usability of cryptocurrencies, attracting more users and investors.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency investing offers exciting opportunities for those willing to navigate its complexities and risks. By understanding the basics, conducting thorough research, and employing sound investment strategies, you can position yourself to take advantage of the potential rewards that the cryptocurrency market offers. Remember to stay informed, continuously educate yourself, and approach cryptocurrency investing with caution and a long-term perspective.
There are many forms of investing in this modern world and who would not want that his/her money should grow just in a matter of time.This is the second blog of our investing series.The previous blog was about investing in stock market.Investing can be called the easiest method of earning money if we learn the technique.It is an example of SMART WORKING. HAPPY INVESTING!
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth overview of the basics of cryptocurrency investing. Feel free to customize or expand on any sections to fit your blog’s style and audience. If you need further details or additional sections, let me know!