Gold
Gold has been a symbol of wealth and prosperity for centuries, playing a crucial role in economies and cultures around the world. Its allure, durability, and rarity make it a unique asset for both business and investment purposes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of the gold business and gold investment, including price fluctuations, karats, hallmarks, and more. By the end of this blog, you will have a solid understanding of the gold market and how to navigate it effectively.
1. Introduction to Gold
1.1 The Historical Significance of Gold

Gold has been valued for its beauty and rarity since ancient times. Civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans used gold for jewelry, currency, and as a standard for trade. Its intrinsic value and universal appeal have made it a preferred store of wealth throughout history.
1.2 The Modern Gold Market
Today, gold plays a significant role in the global economy. It is traded on major exchanges, held by central banks as reserves, and used in various industries, from electronics to medicine. The modern gold market is a complex and dynamic environment, influenced by a range of economic, political, and social factors.
2. The Gold Business
2.1 Gold Mining
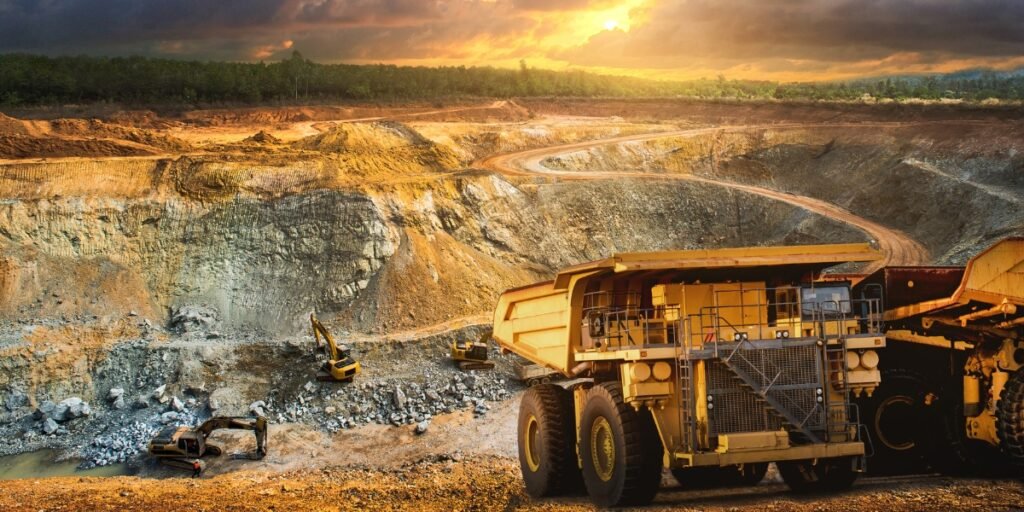

Gold mining is the primary source of newly mined gold. It involves extracting gold ore from the ground and processing it to obtain pure gold. The largest gold-producing countries include China, Australia, Russia, and the United States. Gold mining companies can be a good investment opportunity, offering exposure to the gold market.
2.2 Gold Refining
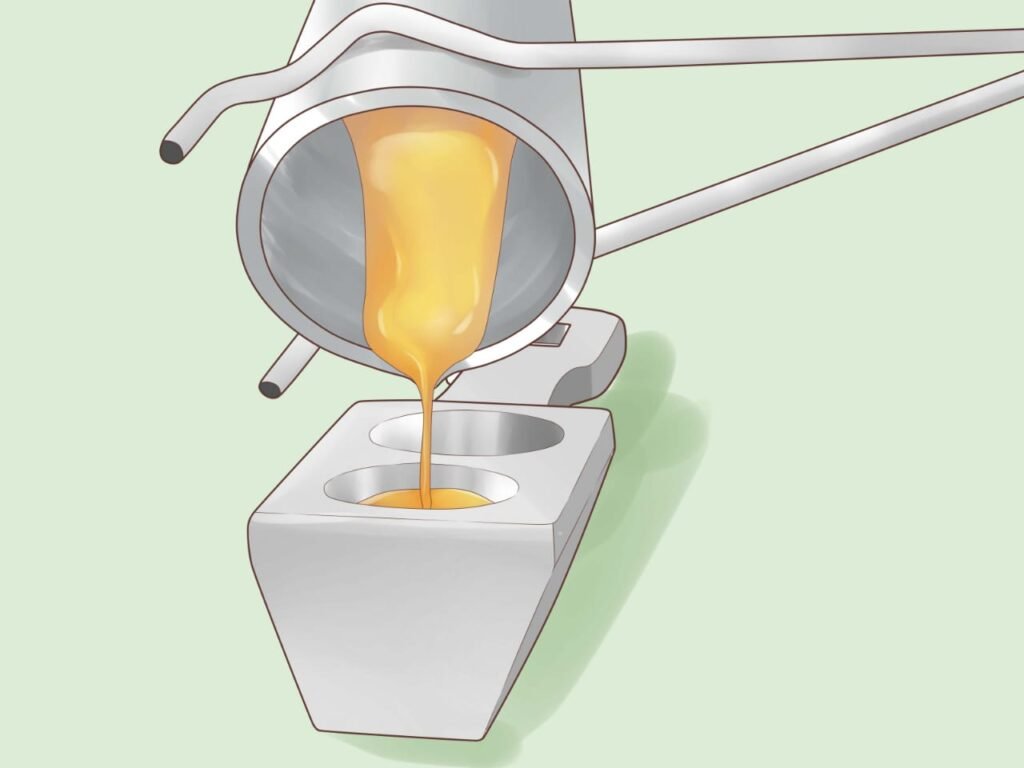
Gold refining is the process of purifying gold to achieve high levels of purity. Refineries remove impurities and produce gold bars or ingots of various purity levels, typically measured in karats or fineness. Refined gold is used in jewellery , investment products, and industrial applications.
2.3 Gold Trading

Gold trading involves buying and selling gold in various forms, such as bullion, coins, and jewellery . Traders and investors can participate in the gold market through physical gold, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), futures contracts, and gold mining stocks. The global gold market is highly liquid, with significant trading volumes on exchanges such as the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) and the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX).
3. Gold Investment

3.1 Why Invest in Gold?
Gold is considered a safe-haven asset, providing stability and protection against economic uncertainties and inflation. Here are some key reasons to invest in gold:
– **Hedge Against Inflation:** Gold has historically maintained its value during periods of inflation, as its price tends to rise when the purchasing power of fiat currencies declines.
– **Diversification:** Gold can help diversify an investment portfolio, reducing overall risk. It often has a low correlation with other asset classes, such as stocks and bonds.
– **Store of Value:** Gold’s intrinsic value and limited supply make it a reliable store of wealth over the long term.
– **Safe Haven:** During times of economic or geopolitical turmoil, investors flock to gold as a safe haven, driving up its price.
3.2 Forms of Gold Investment

Investors can choose from various forms of gold investment, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
– **Physical Gold:** Investing in physical gold involves buying gold bars, coins, or jewellery . While it offers direct ownership and tangible value, it also requires secure storage and insurance.
– **Gold ETFs:** Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) track the price of gold and can be traded on stock exchanges. They offer a convenient and liquid way to invest in gold without the need for physical storage.
– **Gold Mining Stocks:** Investing in gold mining companies provides exposure to the gold market and potential growth opportunities. However, it also involves company-specific risks and market volatility.
– **Gold Futures and Options:** Futures and options contracts allow investors to speculate on the future price of gold. These derivatives can offer significant leverage but also carry higher risk.
3.3 Strategies for Gold Investment

4.1 Factors Influencing Gold Prices
Gold prices are influenced by a variety of factors, including:
– **Supply and Demand:** The balance between gold supply and demand affects its price. Factors such as mining production, central bank purchases, and consumer demand for jewellery play a significant role.
– **Economic Conditions:** Gold prices tend to rise during economic uncertainties, such as recessions or financial crises, as investors seek safe-haven assets.
– **Inflation:** Higher inflation rates erode the purchasing power of fiat currencies, leading investors to buy gold as a hedge, driving up its price.
– **Interest Rates:** Lower interest rates reduce the opportunity cost of holding gold, making it more attractive to investors. Conversely, higher interest rates can pressure gold prices.
– **Geopolitical Events:** Political instability, wars, and conflicts can increase demand for gold as a safe-haven asset, boosting its price.
– **Currency Strength:** Gold is priced in US dollars, so changes in the value of the dollar can impact gold prices. A weaker dollar makes gold cheaper for foreign buyers, increasing demand and driving up prices.
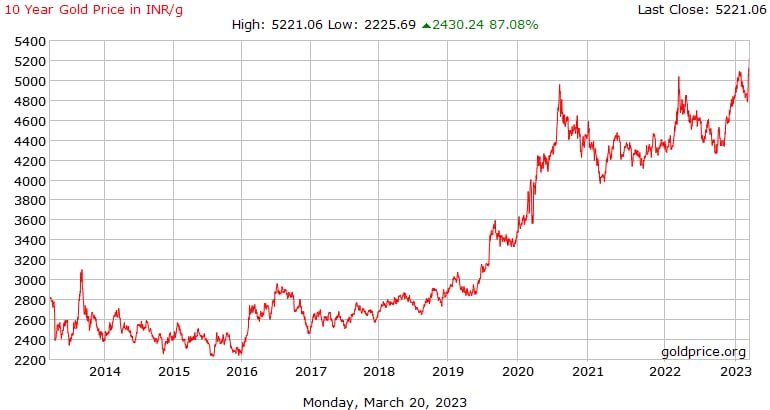
4.2 Historical Gold Price Trends
Gold prices have experienced significant fluctuations over the years. Understanding historical trends can provide insights into potential future movements:
– **1970s:** Gold prices surged during the 1970s due to high inflation, geopolitical tensions, and the collapse of the Bretton Woods system, which ended the US dollar’s convertibility to gold.
– **1980s:** Gold prices peaked in 1980, driven by high inflation and geopolitical uncertainties. Prices then declined as inflation and interest rates were brought under control.
– **1990s:** Gold prices remained relatively stable during the 1990s, as strong economic growth and low inflation reduced demand for gold.
– **2000s:** Gold prices began to rise in the early 2000s, driven by economic uncertainties, rising inflation, and increased demand from emerging markets. The global financial crisis of 2008 further boosted gold prices as investors sought safe-haven assets.
– **2010s:** Gold prices reached an all-time high in 2011 due to economic instability and loose monetary policies. Prices then corrected and remained volatile, influenced by various economic and geopolitical factors.
– **2020s:** The COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in gold prices as investors sought safety amidst economic uncertainties. Gold prices reached new highs in 2020 and continued to fluctuate with changing economic conditions.
5. Understanding Karats and Hallmarks
5.1 What Are Karats?
Karats (kt) are a measure of the purity of gold. Pure gold is 24 karats, meaning it is 100% gold. Because pure gold is too soft for most practical uses, it is often alloyed with other metals to improve its durability. The karat system indicates the proportion of gold in the alloy:

– **24 Karat (24K):** Pure gold (99.9% gold)
– **22 Karat (22K):** 91.7% gold, alloyed with other metals such as copper or silver
– **18 Karat (18K):** 75% gold, commonly used in high-quality jewellery
– **14 Karat (14K):** 58.3% gold, durable and widely used in jewellery
– **10 Karat (10K):** 41.7% gold, affordable and durable
5.2 Hallmarking
Hallmarking is the process of certifying the purity of gold and other precious metals. It involves testing and marking gold items with a stamp or hallmark that indicates their purity. Hallmarking ensures the quality and authenticity of gold products, protecting consumers and promoting trust in the market. The below given image shows Hallmarking done by Indian Standards

5.3 Hallmarking Systems Around the World
Different countries have their own hallmarking systems and standards. Here are some examples:
– **United Kingdom:** The UK has a long-standing tradition of hallmarking, with symbols indicating the assay office, purity, and date of hallmarking. The system ensures high standards of quality and accuracy.
– **India:** India has implemented the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) hallmarking system, which certifies the purity of gold jewellery . The BIS hallmark includes the BIS logo, purity mark, assay center’s mark, and jeweler’s identification mark.
– **United States:** The US does not have a mandatory hallmarking system, but reputable jewelers often use a karat mark to indicate purity. Consumers should look for trusted brands and certification from independent labs like the Gemological Institute of America (GIA).
– **European Union:** The EU has harmonized hallmarking standards, with member countries recognizing each other’s marks. The Common Control Mark (CCM) indicates compliance with the International Convention on Hallmarks.
6. Buying and Selling Gold

6.1 Buying Gold
When buying gold, it’s essential to consider factors such
as purity, authenticity, and pricing. Here are some tips for buying gold:
– **Research and Compare:** Research different types of gold products, such as bullion, coins, and jewellery . Compare prices from various dealers and online platforms to get the best deal.
– **Check Purity:** Ensure that the gold you buy is of the desired purity. Look for hallmarks or certification marks that indicate the gold’s purity and authenticity.
– **Buy from Reputable Sources:** Purchase gold from reputable dealers, jewelers, or online platforms with a proven track record. Check reviews and ratings to ensure reliability.
– **Consider Premiums:** Gold products often come with premiums above the spot price of gold. These premiums cover manufacturing, distribution, and dealer margins. Compare premiums and choose products with reasonable markups.
– **Secure Storage:** If buying physical gold, consider how you will store it securely. Options include home safes, bank safe deposit boxes, and specialized storage facilities.
6.2 Selling Gold
Selling gold requires careful consideration to get the best value. Here are some tips for selling gold:
– **Evaluate Market Conditions:** Monitor gold prices and market trends to determine the best time to sell. Selling during periods of high prices can maximize your returns.
– **Get Multiple Quotes:** Obtain quotes from multiple buyers, such as jewelers, pawnshops, and online gold buyers. Compare offers to ensure you get a fair price.
– **Check Purity and Weight:** Ensure that your gold is accurately weighed and its purity is verified. Buyers will often test the gold to determine its value.
– **Consider Transaction Fees:** Be aware of any fees or commissions that buyers may charge. These fees can impact the overall value you receive for your gold.
– **Choose Reputable Buyers:** Sell your gold to reputable buyers with positive reviews and a transparent buying process. Avoid unscrupulous buyers who may offer unfair prices.
7. Risks and Challenges in the Gold Market
7.1 Market Volatility
Gold Volatility means the rate of change of gold prices in a period of given time .Gold prices can be highly volatile, influenced by various economic, political, and social factors. Investors must be prepared for price fluctuations and potential short-term losses.
7.2 Regulatory Risks
Changes in regulations and policies related to gold mining, trading, and investment can impact the gold market. Investors should stay informed about regulatory developments and their potential effects
7.3 Counterparty Risk
When buying or selling gold, there is a risk that the other party may not fulfill their obligations. This risk is higher when dealing with unknown or untrusted buyers and sellers. Using reputable dealers and platforms can mitigate this risk.
7.4 Storage and Security
Physical gold requires secure storage to protect against theft and damage. Storing gold at home carries risks, while using external storage facilities involves additional costs and trust in third parties.
7.5 Liquidity
While gold is generally a liquid asset, selling large quantities or specific gold products may take time and effort. Investors should be aware of potential liquidity challenges and plan accordingly.
8. The Future of the Gold Market

8.1 Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology, such as blockchain and digital gold, are transforming the gold market. Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in the supply chain, while digital gold platforms offer new ways to buy, sell, and trade gold.
8.2 Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
There is a growing focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing in the gold industry. Initiatives such as responsible mining practices and certification programs aim to ensure that gold is produced in an environmentally and socially responsible manner.
8.3 Economic and Geopolitical Factors
The gold market will continue to be influenced by economic and geopolitical factors, such as inflation, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical tensions. Investors should stay informed about global developments and their potential impact on gold prices.
8.4 Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a significant role in the gold market, both as buyers and holders of gold reserves. Changes in central bank policies, such as interest rate adjustments and gold reserve management, can impact gold prices and market dynamics.
9 Conclusion
Gold remains a valuable and versatile asset for both business and investment purposes. Understanding the intricacies of the gold market, from mining and refining to trading and investment, is crucial for navigating this dynamic environment. By considering factors such as price fluctuations, karats, hallmarks, and various investment strategies, you can make informed decisions and effectively manage the risks associated with gold. Whether you are a seasoned investor or a newcomer to the gold market, this comprehensive guide provides the knowledge and insights needed to succeed in the world of gold business and investment.
This detailed guide covers the essential aspects of the gold business and gold investment. Feel free to expand on any sections or add more details to tailor the content to your specific needs. If you have any further questions or require additional information, please let me know!
For enquiries related to kitchen products-CLICK HERE
Youtube Channel –CLICK HERE
FACEBOOK PAGE-CLICK HERE
FACEBOOK GROUP-CLICK HERE
INSTAGRAM ACCOUNT-CLICK HERE